The Future of Solar Energy| MIT Energy Initiative

Future of Solar Energy
Solar energy is the one and only future of all energy needs of ours. Till now we have scratched the outer surface if the sun’s immense potential. The energy that sun gives is many fold more than what we used every year. The continuous endeavor of researchers across the globe is to improve a better technology to collect the sunrays so that better and more efficient devices can be powered by the sun and store this energy for longer periods.
India’s initiative of 100 GW of solar energy by 2022 is a target that we will achieve.
The future of solar energy considers only two widely recognized class of technologies for converting solar energy into electricity. They are Photovoltaic’s (PV) and Concentrated Solar Power (CSP).
The most efficient way is the most common photosynthesis. The future of solar power has looked increasingly bright in recent years due to reducing cost of silicon solar panels and global push for clean energy source to address climate change.
Off Grid and On Grid – Which one is better🤔 ?
On Grid:System generated power directly connected to the utility feed. On grid system sends excess power generated to the utility grid when over produced. These are most cost effective and simplest system to install. Such systems will pay for themselves by offsetting the bill in 3-8 years. On grid system can either be put into place with our without net metering. In case of an On grid system with net metering, calculating the monthly electricity bill, the solar power fed to the grid is netted at the same tariff at which the grid power is available for the consumer. In case of system without net metering the rate at which the solar energy fed is credited can be different from the normal utility tariff. The biggest downfall of On grid system is that it does not provide power during a grid outage.
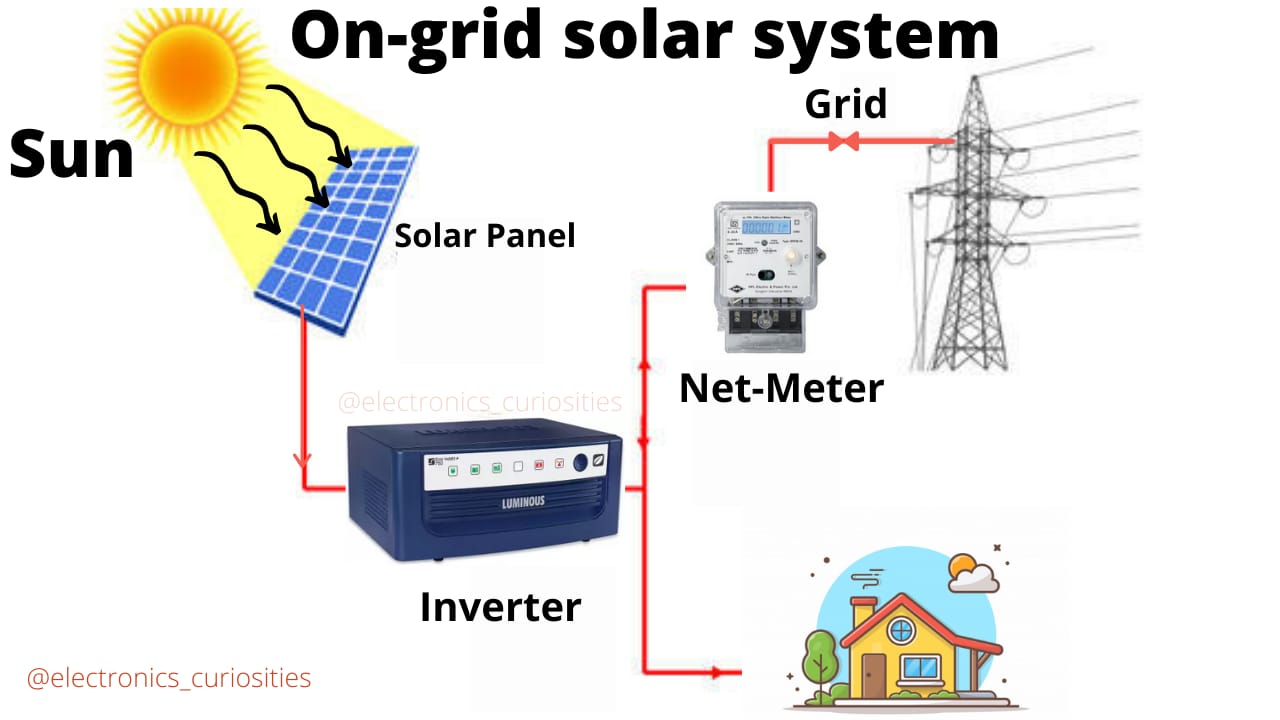
On Grid Solar System
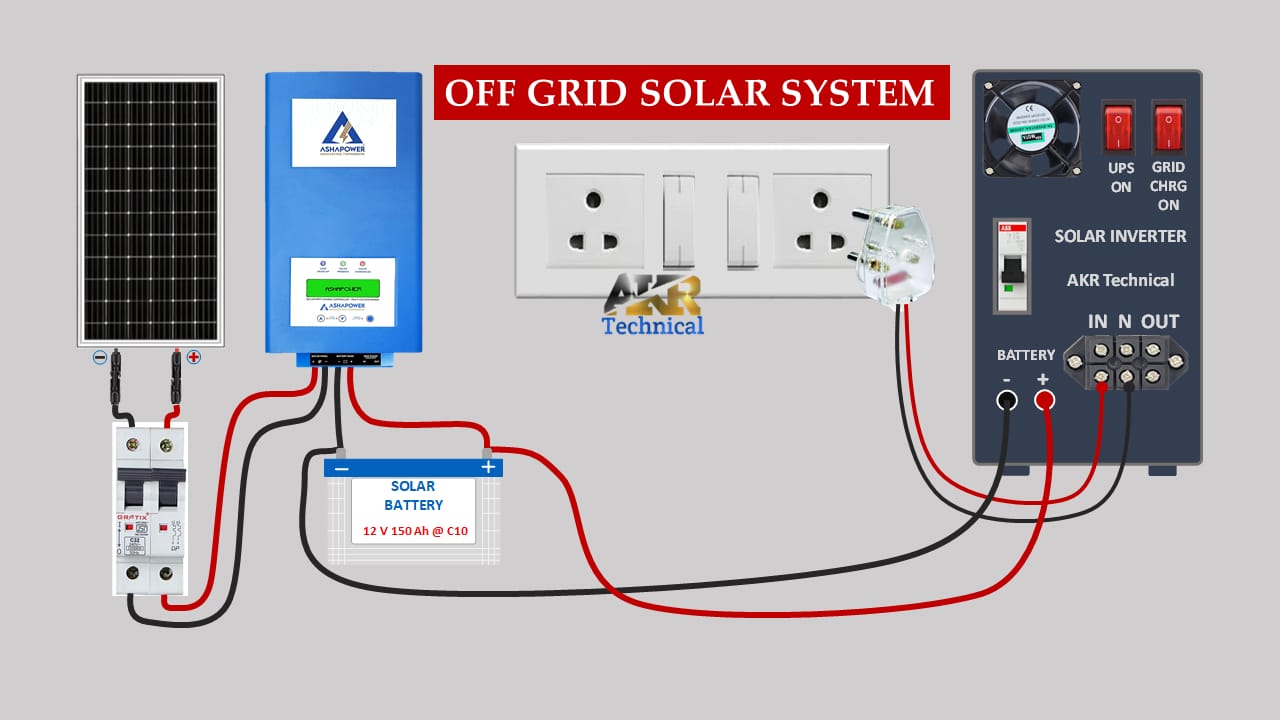
Off Grid Solar System
Off grid system allow you to store and save your solar power in batteries for use when the power grid goes down. It is meant to be entirely self sustaining. One of the best part about off grid solar system is that they do provide power for critical loads when the power grid is down. The biggest downside of the off grid system is that they cannot cater to power demands of all your loads since the cost and volume of batteries would be prohibitive. Such system require a lot more specialized equipments to function. These systems are not only of high cost and complex to install but are can be also not very environment friendly.Another major con of the off grid system is that one cannot completely rely on backup.
The main point boils down to the fact that off grid system is not recommended for average home users. They are neither cost effective nor easily installable.
How solar energy can increase your business profits
Prices of oil and fossil fuels begin to rise by leaps and bonds. Every day the price of fossil fuels increases and imparting a heavy burden on whole economy. Under this circumstances solar energy can be utilized advantageously for reducing utility bills and thereby everybody can enjoy more profit in business.
New material known as ‘Pervoskites’ have been incorporated into solar cells have increased cell efficiency from 3.8% in 2009 to just over 20% in 2014.If technology development in solar continues at this pace, in a few short years this energy source will be able to compete head to head with traditional fossil fuels.
Another reason that the price of solar has dropped recently due to increase in supply from Chinese produces which is putting downward pressure on prices. Most state government offers some sort of tax subsidy to encourage more wide spread solar panel users. As a result the final cost after installation may be reduced to moreover tax credits given for solar power could reduce annual tax bill.
Besides net metering allows utility consumer to generate their own solar electricity to fed some of the energy that they don’t use back to the grid. This billing method credits the solar customer against their electricity consumption, lowering their monthly bill.
For commercial and industrial users of electricity, the tax incentives offered on solar power plant by the GOI are quite attractive, and make adoption of solar power a thriving and sustainable reality. To encourage the adoption of solar power by commercial and industrial users, GOI offers accelerated depreciation of capital assets associated with solar power plant. The current rate of acceleration which can be claimed in a year is 40%.
For our calculation & simplifications let us consider an example:-
The accelerated depreciation benefit allows the commercial and industrial users of solar power to depreciate the assets built as Solar Power Plant at a much higher rate than general capital assets.
This allows the user to then claim tax benefit on the value depreciated in a given year.
The following example further illustrates the point –
- Let’s say a commercial or industrial user, HOPEDWELL ENERGY SOLUTIONS PVT.LTD falls under an income tax bracket of 30%. Now suppose this user builds a general asset that is valued at Rs. 50 LAKH in a given financial year, with an expected asset life of 20 yrs. Under normal circumstances, the user will be able to claim an annual depreciation of 5% of Rs.50 LAKH (considering linear depreciation, 100%/20yr = 5%/yr). for purpose of income tax.
- This means the user will be able to claim tax benefit of 30% of 5% of Rs. 50 LAKH per year = Rs. 75000 per year for next 20 years.
- However, in case of same investment made in a Solar Plant, the user is allowed to depreciate the asset at 40%, thus allowing the user to completely depreciate the asset within three years term, and saving a tax of Rs. 6 Lakh, Rs. 6 Lakh and Rs. 3 Lakh in the first, second and third year of operation respectively.
- For anyone who appreciates time and value of money, the proposition of saving Rs. 15 lakh in taxes within only the first three years of installing the PV system is lucrative compared to saving the same amount over a period of twenty years. Thus the project IRR (internal rate of return) increases by the virtue of accelerated depreciation.
- The rate of accelerated depreciation on solar power plants has been reduced from 80% in FY16-17, to 40% in FY17-18 onwards.

